What is Folic Acid? Is folic acid a vitamin?
Folic acid (also known as folate or vitamin B9) is an essential nutrient; it plays important role in many cell functions and is useful in cell development and replication, hair and nail growth, and the prevention of atherosclerosis and neural tube birth defects.
Folic acid deficiency can be caused by poor diet, alcoholism, surgery, pregnancy, and malabsorption-causing digestive disorders such as Crohn’s and celiac diseases. Supplementation of folic acid is also important for patients on certain medicines, such as methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis, as these medications can reduce folate in the body. Folate deficiency can have serious side effects, so treatment (especially during early pregnancy) is important. A folic acid iv drip or injection can help improve low folate levels.
Is folic acid the same as folate?
The terms folic acid and folate are often used interchangeably despite being different forms of vitamin B9.
B9 is a water-soluble essential nutrient that occurs naturally as folate. Folic acid is a synthetic form of folate used in dietary supplements and fortified foods. While folate is digested in the stomach and converted into its active form, folic acid is only partially processed via digestion. It also needs converting in your liver and other tissues.
Folic Acid Deficiency Symptoms
The biggest side effects of folic acid deficiency are anemia and birth defects. Pregnant women who don’t get enough folate intake put their babies at risk for brain and spinal cord defects.
Other symptoms of folic acid deficiency include:
- depression
- fatigue and low energy
- pale skin
- shortness of breath
- muscle weakness

Folic acid during pregnancy
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend women of childbearing age get 400 micrograms of dietary folate equivalents (DFE) every day. Folic acid is essential for the prevention of neural tube defects (NTDs) and is most important 1 month before conception and during the first 3 months of pregnancy.
Nearly half of pregnancies in the US are unplanned. So, everyone capable of becoming pregnant benefits from making sure to get enough folic acid.
The CDC also reports that increased folic acid intake in pregnant people with an MTHFR variant can also help reduce the risk of NTDs in their baby. People with a specific variant of the MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) gene have an impaired ability to break down and use folate. There is currently no evidence of other types of folate intake reducing NTD occurrence, but even with an MTHFR variant, increased folic acid intake benefits your unborn baby.
Folic acid while breastfeeding
Even after birth, adequate folic acid intake is paramount. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) considers folic acid supplementation compatible with breastfeeding.
Folate deficiency can have serious side effects, so treatment (especially during early pregnancy) is important.
Folic Acid Benefits
Wondering why folic acid is important? Folic acid benefits just about every part of the body. Folic acid plays a role in the synthesis and repair of DNA and RNA as well as the growth of healthy cells. It is used for the production of red blood cells and brain health.
Folic acid can help many other things, such as:
Sperm Count
One of the main folic acid benefits for men is to aid in correcting sperm counts and motility.
Menstruation
Folic acid is important in women’s health for many reasons, including its role in hemoglobin production. Heavy menstrual cycles often lead to loss of hemoglobin and deficiency in iron levels.
Heart Disease
Along with vitamin B12, folic acid plays an important role in cardiovascular health and function. Folate helps manage homocysteine levels and reduce the risk of blood clots thus helping reduce the chances of heart attacks.
Cancer
The Journal of the National Cancer Institute has reviewed clinical trials that suggest folic acid plays a protective role against colon cancer, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
Depression
Folic acid is used to enhance mood regulation and treat depression symptoms. Proper brain functioning requires adequate folic acid levels.
Digestion
Vitamins B12 and C work with folic acid to help the body digest and utilize proteins.
Acne
Folic acid helps in eliminating toxins from the body, which can reduce acne on the face.
Hair Growth
Folic acid renews the cells that aid the growth of hair. Folic acid deficiency can lead to premature graying and hair loss.
Red Blood Cells
Folic acid plays an important role in white and red blood cell production.
Skin Health
Folic acid helps in reducing the signs of skin aging, improves the firmness of the skin, and helps in the production of healthy skin.
Diabetes
Folic acid helps prevent type 2 diabetes by reducing fat content in the blood.
Folic acid in pregnancy
As previously mentioned, folic acid is incredibly important before and after conception – which is why it’s included in prenatal vitamins. Folic acid protects your baby from multiple birth defects including:
- spina bifida – a spinal cord defect
- anencephaly – missing parts of the brain or skull
- cleft lip and palate
- low birth weight
Folic Acid Rich Foods
In 1998, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) required that enriched grain products such as bread, rice, pasta, and breakfast cereal also have folic acid fortification.
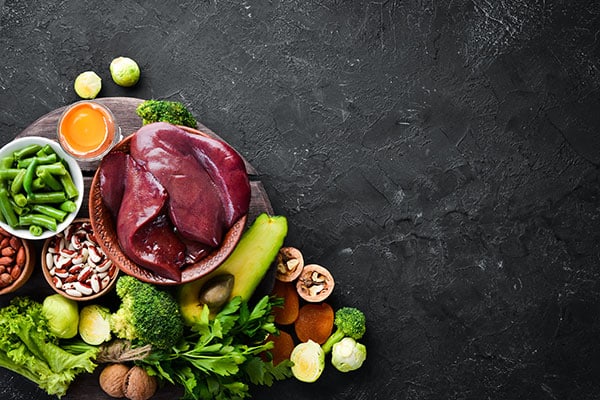

Other folic acid high foods include:
- leafy vegetables (e.g., spinach, collard greens)
- dark green vegetables (e.g., broccoli, brussels sprouts)
- potatoes
- beans
- fruits
- organ meat (e.g., liver, kidneys)
Be aware that cooking foods may reduce the amount of folic acid in them. And while multivitamins and B-complex vitamin supplements can help supplement your folate intake, they are not a complete replacement for a healthy diet.
If you’re planning to become pregnant, you might need extra supplementation to reach the recommended 400 mcg of folic acid per day.
Folic Acid Risks
Folate is water-soluble, meaning excess folate in the body will be removed in the urine. So, it’s hard to “overdose” on folate.
However, if you’re undergoing medical treatment for cancer, epilepsy, or kidney dialysis, talk to your healthcare provider before beginning any folic acid supplementation. Folic acid can decrease the effectiveness of some medications, including phenytoin for epilepsy or methotrexate for cancer treatment.
High folic acid intake can also mask symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency. One sign of B12 deficiency is megaloblastic anemia, which can be corrected by high doses of folic acid. But folic acid won’t correct the other problems caused by B12 deficiency.
Before beginning any vitamin supplementation, be sure to consult with a healthcare provider. At our clinic, we’re also able to perform bloodwork to check for any vitamin deficiencies.
Why choose IV Vitamin Therapy for folic acid injections?
IV Vitamin Therapy is located in a lovely boutique-style medical office. The process is almost entirely painless, nothing but a quick needle prick. Almost immediately after injection, the nutrients injected into the body begin working.
Folic acid injections near me
Busy? We’ll come to you. Many of our clients who prefer to receive injections in the privacy of a home or office can choose our popular concierge house call service.
IV Vitamin Therapy is the practice to trust for IV vitamin therapy. We are conveniently located in Beverly Hills and can come to your home or office throughout the Los Angeles area. We serve patients near Beverly Hills, Bel Air, West Hollywood, Santa Monica, West Los Angeles, Culver City, Hollywood, Venice, Marina del Rey, Malibu, Manhattan Beach, Redondo Beach, Downtown Los Angeles, Encino, Woodland Hills, Sherman Oaks, Calabasas, Burbank, Glendale, Hidden Hills, Agoura Hills, Northridge, North Hollywood, Topanga, Canoga Park, Reseda, Valley Glen, Chatsworth, West Hills, Winnetka, Universal City, Silverlake, Echo Park, and many more.
Book now at 877-760-3564


